Residual Tumor-Free Mucin Ponds In Mastectomy Material After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Global Journal of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine
Volume 1, Issue 6, July, Pages: 3-4
Received: June 08, 2022, Reviewed: June 15, 2022, Accepted: June 30, 2022, Published: August 3, 2022
Unified Citation Journals, Pathology 2022, 1(6) 5-9; https://doi.org/10.52402/Pathology215
ISSN 2754-0952
Author: Asst. Prof. Dr. Alptekin Şen
Istanbul Demiroğlu Bilim University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pathology, Istanbul/Turkey
SUMMARY: Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is a rare type of breast cancer. As in other types of breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy is applied to shrink the tumor before surgery or due to oncological indication. These chemotherapy applications may result in remission at different rates. However; The interesting thing about these cases is that, as observed in our case, even if complete remission is achieved with medical treatment, the presence of mucin ponds accompanying the tumor continues at different rates without the presence of the tumor.
KEYWORDS: Breast mucinous carcinoma, neodjuvant will be, complete remission, mucin ponds.
INTRODUCTION:
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is a relatively rare subtype of breast cancer, accounting for approximately 2% of all breast carcinomas. (1) The prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma is generally good. (2) What is interesting is; As in our case, it is the presence of mucin ponds that remain residual by showing resistance that tumor cells cannot show after chemotherapy.
Our case is a 43-year-old woman. In May 2021, she was diagnosed with ‘mucinous carcinoma ‘ as a result of a true-cut biopsy performed at the center outside our hospital where she applied with the mass she noticed in her right breast . As a result of the oncological and surgical evaluation of the patient, 6 months of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is prescribed. At the end of the period, the patient was admitted to our center and underwent right subcutaneous mastectomy + axillary dissection. In the operation materials examined in our laboratory; A mastectomy material with a thickness of 5 cm, covered with a skin ellipse of 17×1.5 cm., had a 2×1.5×1.5 cm in size, completely mucinous-gelatinous, irregular area in the area corresponding to the upper outer quadrant. A total of 19 lymph nodes with a diameter of 3.5 and the smallest with a diameter of 0.3 cm were dissected from the axillary dissection material.
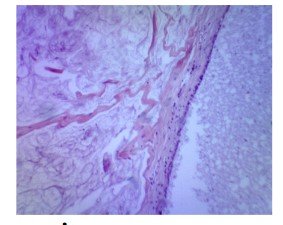
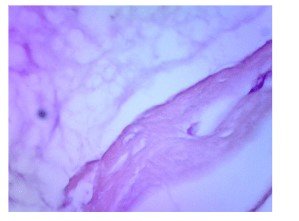
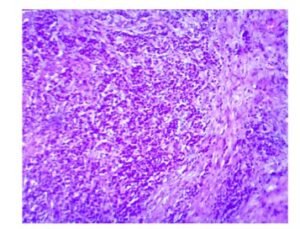
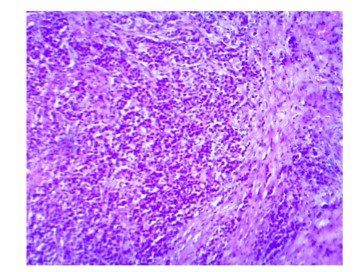
In histopathological sections of the mutilated area of the mastectomy material defined on macroscopy; In addition to ductal hyperplasia and cystic change areas , large mucin ponds are observed ( pictures 1 and 2)
İmage 1: H&E X4 İmage 2: H&Ex40
Although the entire lesion and most of the breast were examined, no residual tumor tissue was observed.
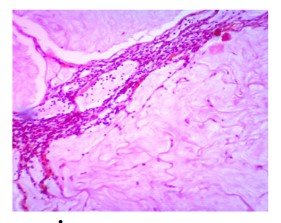
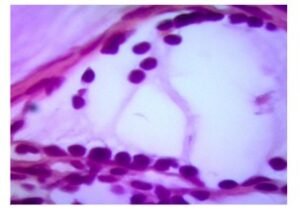
In 4 of the lymph nodes dissected from axillary dissection material, mucin ponds similar to those in the breast are located, but no residual tumor is observed. (images 3 and 4)
İmage 3: H&E X 4 İmage 4: H&E X40
In other lymph nodes; reactive changes were monitored. (Image 5)
İmage 5: H&E X 4
In this context, we believe in the fact; It was diagnosed as ‘complete remission findings after neoadjuvant chemotherapy’ and pT category was evaluated as ypT0.
CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION:
Mucinous carcinomas usually grow slowly and can reach large sizes at the time of diagnosis. 5) Most of the patients present by palpating the breast mass. (6)
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is a standard use for patients who are inoperable or have smaller tumors and for whom surgical administration is more beneficial after chemotherapy. (3)
Histopathological evaluation of the surgical procedure material performed routinely after the procedure will reveal both the effect of chemotherapy and the adequacy of surgical treatment. When evaluated with WHO criteria; Breast tumors with mucin components are defined as ‘mucinous carcinomas’ (3)
However; An evaluation of mucinous carcinomas without tumor after chemotherapy according to the presence or amount of mucin has not been done in a very healthy way. In mucinous carcinomas evaluated after NAC; There are studies that show that the presence of mucin ponds has no effect on overall survival. (4)
In another study, tumor size was also included and especially in pure mucinous carcinomas; It was concluded that tumor size and volume of mucin ponds had no effect on prognosis. (5)
After all; In patients undergoing breast surgery after NAC, the contribution of the amount of mucin deposits to the prognosis can be demonstrated by larger series of studies. These studies may indicate a good response to NAC, as opposed to the presence of this mucin and residual tumor. (3)
REFERENCES:
- Faten L, Faren A, StatPearls (Internet). Teasure Island (FL) :StatPearls Publishing ; 2022-jun
- Meng Y,Xin L, Pang Chun-Hong,Huang Lin-Ping ,Breast Care (Basel) 2013 March ; 8(1) :56-59
- Maria J , Eldo V, Nisha S, Sally L , BMJ litigation representative 2016 May
- Bhatti AB, Akbar A, Khattak S et al., Effect of acelular mucin pools on survival in patients with complete pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy,Int J Surg 2014 ;12:1123
- Komenaka IK, El-Tamer MB, Troxel A, Hamele-Bena D , Joseph KA, Horowitz E, Ditkoff BA, Schnabel FR, Memenin Musinöz karsinomu . Am J Surg .2004 Nisan 187 (4) :528-32
- Wilson TE, Helvie MA, Oberman HA, Joynt LK, Pure and mixed mucinous carcinoma of the breast. AJR J Röntgenol .1995 Aug ;165 (2) : 285-9
© Copyright 2022, All Rights Reserved. Use of this content signifies your agreement to the T&Cs of Unified Citation Journals
This abstract of Manuscript/Paper/Article is an open access Manuscript/Paper/Article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which allows and permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and accepted.
This communication and any documents, or files, attached to it, constitute an electronic communication within the scope of the Electronic Communication Privacy Act (https://it.ojp.gov/PrivacyLiberty/authorities/statutes/1285)
To citation of this article: Asst. Prof. Dr. Alptekin Şen, Residual Tumor-Free Mucin Ponds In Mastectomy Material After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Global Journal of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine