Medical Tourism: Gains And Burdens In Developing Countries
Dr. Phuc Hong Ngoc Nguyen
Unified Nursing Research, Midwifery & Women’s Health Journal
Author: Dr. Phuc Hong Ngoc Nguyen
Affiliation: Faculty of Public Health – University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City
Category: Abstract
Unified Citation Journals, 2(1) 12-14; https://doi.org/10.52402/Nursing2013
ISSN 2754-0944
Keywords: Medical tourism, health tourism, health economics, supply and demand, developing countries
Introduction:
Medical tourism has been growing quite actively in the last few decades. Patients, especially from developed countries, are increasingly seeking medical care across national borders. While in the past people from the East travelled to the West to seek for the best healthcare services, nowadays, Western people come
to the East to seek for the best medical technologically advanced healthcare with more affordable expenditure.
For that, in most cases, Low- and Middle-income countries are more likely to be the best options. The growth
of medical tourism emphasizes the privatization of healthcare, uneven access to health resources and the accelerated globalization of both healthcare and economics in every involved countries. Low- and Middle-income countries, however, are more likely to be effected in multi dimensions.
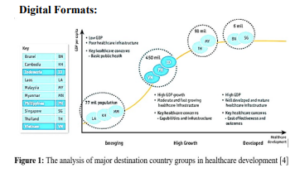
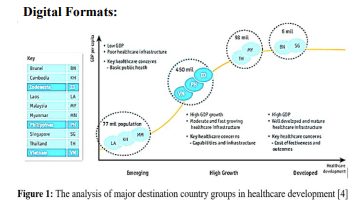
How does medical tourism pose impacts on developing countries?: Medical tourism brings certain advantages along with important disadvantages to developing countries. It significantly contributes to GDP of destination countries by the tax collected from the demanding health services. Besides of the financial benefits for the economic development as it creates more jobs, health care facilities, access to latest and greatest modern technology that improve the quality of life of everybody involved, the phenomenon has put a significant improvement in some key implications of health systems in developing countries. Medical tourism does, however, create unintended consequences for destination nations including the growth of health disparities, inequality, patients and community safety, ethical violation, and reversed costs in these involved countries.
Digital Formats:
Conclusion: To keep being ahead, medical tourism should be seriously and professionally managed at different perspectives with the involvement of not only healthcare professionals but also governments and other professionals in various expertise.
References:
[1] Al-Lamki L. et al. (2011) Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J, 4:444-7.
[2] Bartold PM. (2014) Aust Dent J.59 (3): 279.
[3] COMCEC (2020) Joint Commission International 54-57.
[4] Sompeeti Wallibhodome (2019) Kenan Institute Asia J. 13140.
[5] Viktoriia Vovk et al. (2021) Int J Environ Res Public Health, 18 (21): 11205.
Upcoming Conferences;
- 13th American Healthcare & Hospital Management Summit from November 15-18, 2023 in Los Angeles, USA.
More Details: https://health.universeconferences.com/ - 13th World Nursing, Healthcare Management, and Patient Safety Conference in Los Angeles, USA on November 15-18, 2023.
More Details: https://nursing.universeconferences.com/ - 13th International Nursing, Healthcare and Patient Safety Conference from July 25-27, 2024 in Holiday Inn Dubai, UAE.
More Details: https://nursing-healthcare.universeconferences.com/