Electronic water can reduce oxidative stress in cancer and diabetes patients for 3 weeks drinking
Global Journal of Diabetes, Endocrinology & Metabolic Disorders
Volume 1, Issue 1, June 2020, Pages: 20-28
Received: Mar. 17, 2020; Accepted: Apr. 17, 2020; Published: Apr. 27, 2020
Authors: Dr. Masahiro Onuma, President of Trisguide ltd Japan
Abstract:
Oxidative stress means a state there is an imbalance between the oxidizing action and the reducing action due to reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a living body, resulting in the oxidizing action becoming dominant. Oxidative stress arises as the balance between production and removal is disrupted through excessive production of ROS and impairment of the antioxidant system. Oxidative stress has been reported to be involved in the onset and progress of various diseases.
Characteristics of Type 2 diabetes are insulin secretion failure and insulin resistance, but it seems that oxidative stress is greatly involved in insulin secretion failure. In the insulin secretion-inducing β cells of Langerhans islets in the pancreas, the amount of superoxide dismutase (SOD), which is representative of the ROS elimination system, is small and resistance to oxidative stress is considered to be weak. Regarding cancer, it is well known that chronic inflammatory conditions increase the risk of carcinogenesis. Cells such as neutrophils and macrophages are activated in the inflammation area leading to an increase in the production of active oxygen and nitric oxide. These free radicals cause DNA mutation and cell proliferation thereby promoting cancer development. When chronic inflammation is present, cancer develops more easily.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes, Chronic Inflammatory, DNA Mutation, Oxidative Stress.
Download Full Article & Abstract here:
Copyright
© Copyright 2020, All Rights Reserved. Use of this content signifies your agreement to the T&Cs of Unified Citation Journals
This abstract of Manuscript/Paper/Article is an open access Manuscript/Paper/Article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which allows and permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and accepted.
This communication and any documents, or files, attached to it, constitute an electronic communication within the scope of the Electronic Communication Privacy Act (https://it.ojp.gov/PrivacyLiberty/authorities/statutes/1285)
To citation of this article: Masahiro Onuma, Electronic water can reduce oxidative stress in cancer and diabetes patients for 3 weeks drinking, Global Journal of Diabetes, Endocrinology & Metabolic Disorders
References:
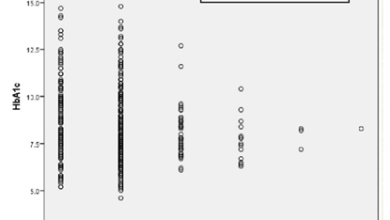
Electronic water, which was developed to generate electron in water, was consumed for three weeks, after meals, between meals and before sleeping 6 times a day, and according to the test subjects’ possible time periods. The amount of drinking water was 750-1000 mL, and BAP and d-ROMs checks for all cases were carried out at 4:30 pm. The results of cancer patients and diabetes patients were seen as attached.
As a result, the d-ROMs value in the degree of oxidative stress has reduced, and the BAP value, which is an indicator of plasma antioxidant capacity, has improved significantly.
Tags
Therapeutics Cancer Journals | Molecular Oncology Genes Cancer Journals | Epigenetics Advances in Cancer Research Journals | Oncologist Molecular Cancer Research Journals | Gastric Cancer Journals | British Cancer Journals | European Cancer Journals | Cancer Carcinogenesis Journals | Radiation Oncology Journals | Cancer Prevention Research Journals | Cell death & disease Oncogenesis Journals | Endocrine-Related Cancer Journals | Angiogenesis Cancer Journals| Immunology and Immunotherapy Cancer Journals | Science Lung Cancer Journals