Presented in 5th International Neurosurgery and Neurological Surgeons Conference from January 14–16, 2026, in Dubai, UAE & Online.
Speaker Name: Mr. Mohamed Elhendawy
Organization: University Hospital of Wales ( NHS United Kingdom )
Location: United Kingdom
Category: Speaker/Oral Presentation
Biography: Mr Elhendawy has completed his training in neurosurgery and currently working as a senior fellow at university hospital of Wales United Kingdom. He holds dual fellowship qualifications from the Royal College of Surgeons in England (RCS) and the European Association of Neurosurgical Societies (EANS). He has a particular interest in neurovascular and neuro-oncology subspecialities.
Unified Journal of Neuroscience (UJN)
Visit Speaker Page here: https://neurosurgery.utilitarianconferences.com/speaker/mrmohamed-elhendawy
Mr Mohamed Elhendawy, FRCS(SN), FEBNS, University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff, UK.
Introduction: Cerebral vasospasm is a major cause of delayed cerebral ischaemia (DCI) following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (aSAH) [1]. Sympathetic blockade via stellate ganglion block (SGB) improves cerebral perfusion by reducing cerebrovascular tone [2].
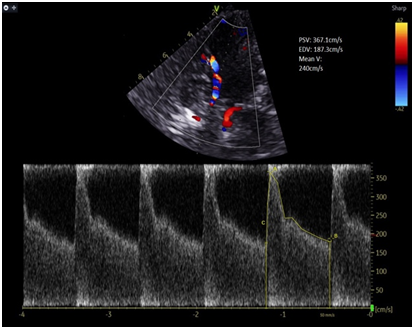
Case Description: A 53-year-old gentleman presented with a modified Fisher grade IV subarachnoid haemorrhage secondary to a ruptured anterior communicating artery (ACOM) aneurysm, treated with endovascular coiling. On post-bleed day 4, he developed symptomatic vasospasm. Despite maximal therapy including oral and intra-arterial nimodipine and hypertensive therapy in the intensive care unit, his neurological condition deteriorated. An ultrasound-guided left stellate ganglion block at C6/7 level was performed using 8 mL of 0.5% levobupivacaine with clonidine 75 mcg. The patient demonstrated immediate neurological improvement, with a reduction in left middle cerebral artery transcranial Doppler (TCD) mean velocity from 246 cm/s to 110 cm/s, without any procedural complications.
Conclusions: Ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block may represent a safe and rapidly effective adjunctive treatment for refractory cerebral vasospasm following aSAH. Larger studies are needed to further evaluate its utility and establish clinical guidelines [2,3].
Keywords: Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage; cerebral vasospasm; stellate ganglion block; cervical sympathetic block; neurosurgery.
References:
[1] Vergouwen M. D. I. et al. (2010) stroke, 41, 2391-2395. [2] Wendel C. et al. (2019) J Neurosurg., 133,773-779. [3] Oliveira L. B. et al. (2024) World Neurosurg., 182,124-131.
Tag:
Upcoming Conference:
Visit here: https://neurosurgery.utilitarianconferences.com/
Submit your abstract/research paper here: https://neurosurgery.utilitarianconferences.com/submit-abstract
Attend as a Speaker/Poster/Delegate In-person kindly register here: https://neurosurgery.utilitarianconferences.com/registration
Attend as a Speaker/Poster/Delegate virtually kindly register: https://neurosurgery.utilitarianconferences.com/virtual-registration